What the United States Medical Supply TV commercial - New CGM is about.
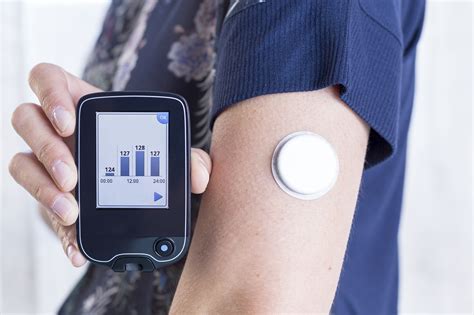
The United States Medical Supply TV Spot introduces its latest product, the New CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitor). The spot opens with a person waking up in the morning, putting on the CGM sensor on their arm. The voice-over then explains how the New CGM works and how it can help people manage their diabetes better.
The spot goes on to show various people going about their daily activities, all the while wearing the New CGM sensor. The voice-over explains how this device can constantly monitor blood sugar levels in real-time, allowing people with diabetes to make informed decisions about their health and lifestyle while avoiding drastic fluctuations in their blood sugar levels.
The CGM also boasts a user-friendly smartphone app that can provide users with daily reports on their glucose levels, helping them to understand and manage their diabetes better. It can also alert users to any sudden changes in their blood sugar levels, making it an essential tool for people with diabetes.
The United States Medical Supply TV Spot ends with a call to action, urging viewers to contact them or visit their website to learn more about the New CGM and how it can help them manage their diabetes. Overall, the spot offers an informative yet engaging message, highlighting the benefits of this innovative medical device while also addressing the concerns of people living with diabetes.
United States Medical Supply TV commercial - New CGM produced for
United States Medical Supply
was first shown on television on December 23, 2022.
Frequently Asked Questions about united states medical supply tv spot, 'new cgm'
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices help you manage Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes with fewer fingerstick tests. A sensor just under your skin measures your glucose levels 24 hours a day. A transmitter sends results to a wearable device or cell phone.
A quick look at the best home glucose meters
- Best overall for new users: The Contour Next One | Skip to review.
- Best for blood-free readings: FreeStyle Libre | Skip to review.
- Most accurate continuous glucose meter (CGM): Dexcom G6 | Skip to review.
- Longest lasting CGM sensor: Eversense |Skip to review.
Unlike a single reading from a blood glucose meter, a CGM provides real-time, dynamic information about the speed and direction (trending higher or lower) of your glucose levels. Having continuous feedback on diet, exercise, and insulin requirements from a CGM can help you make more informed treatment decisions.
The price of glucose monitors via CGM programs can vary from $134 to $399 per month. These programs typically include a shipment of 2 CGMs every month throughout the duration of your subscription. Some companies may require a yearly subscription fee, even if you only intend to use a CGM for one month.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices help you manage Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes with fewer fingerstick tests. A sensor just under your skin measures your glucose levels 24 hours a day. A transmitter sends results to a wearable device or cell phone.
The CGM estimates glucose levels and wirelessly sends the information to a software program on a smartphone or insulin pump. The program calculates how much insulin your body needs, and the insulin pump delivers the insulin when glucose levels rise higher than your target range.
Dexcom G7
Dexcom G7, the simple CGM system, delivers real-time glucose numbers to your smartphone * or smart watch ‡ - no fingersticks required. Effortlessly see your glucose levels and where they're headed, so you can make smarter decisions about food and activity in the moment to take better control of your diabetes.
Two types of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are currently available for daily diabetes self-management: real-time CGM and intermittently scanned CGM.
Professional CGM
The sensor is applied to the back of a patient's upper arm in the provider's office and requires a 2-minute activation period. The system then records glucose levels every 15 minutes for up to 14 days. The patient has no interaction with the sensor and cannot see the glucose data.
CGMs can be used in the hospital to decrease the frequency of fingerstick point of care capillary blood glucose testing, decrease hyperglycemic episodes, and decrease hypoglycemic episodes.
CGM may not be right for everyone. The meters are rather expensive ranging from approximately RS 50000 and up. If you are not experiencing poor diabetes control, then this system or monitor may not be worth the extra price.
The CGM estimates glucose levels and wirelessly sends the information to a software program on a smartphone or insulin pump. The program calculates how much insulin your body needs, and the insulin pump delivers the insulin when glucose levels rise higher than your target range.