Ingrezza tv commercials
TV spots
TV commercials Ingrezza



Advertisers
Advertisers of commercials featuring Ingrezza
Ingrezza
IntroductionIngrezza is a drug developed by Neurocrine Biosciences, a pharmaceutical company based in California, United States. It is the first FDA-approved treatment for tardive dyskinesia (TD), a m...
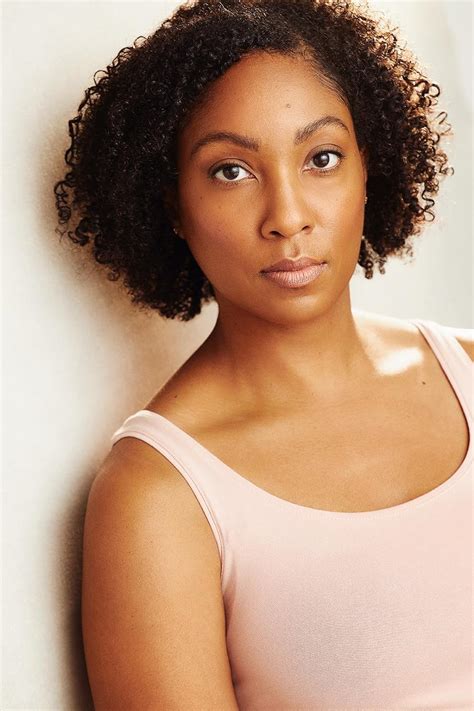
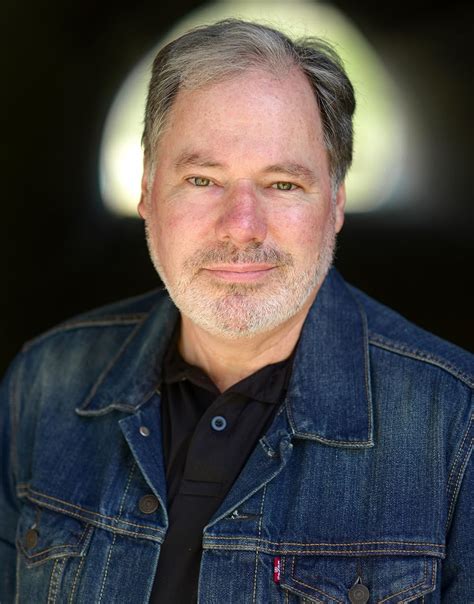
Actors
Actors who starred in Ingrezza commercials
What is Ingrezza?

Ingrezza is a prescription medication primarily used to treat adults with tardive dyskinesia. This condition is characterized by uncontrollable movements of the face and body, often caused by long-term use of certain medications. Ingrezza works by regulating the levels of dopamine in the brain, which is a chemical that is involved in the control of movement.
The medication is available in capsule form and is usually taken once daily. The dosage is typically determined by a healthcare provider and may be adjusted based on the individual's response to the medication. Ingrezza is known to be effective in reducing the severity of tardive dyskinesia symptoms, such as facial grimacing, tongue protrusion, and repetitive movements of the arms, legs, and torso.
Although Ingrezza is generally well-tolerated by most patients, the medication can cause certain side effects, including sedation, dry mouth, and akathisia, which is an inner restlessness. Patients taking Ingrezza should not consume alcohol, as it can increase sedation and impair cognitive function.
It is important to note that Ingrezza may not be suitable for everyone, especially for women who are pregnant or may become pregnant, as it can cause harm to the developing fetus. Before starting Ingrezza, patients should inform their healthcare provider about any other medications they are taking, as well as any medical conditions they may have.
In summary, Ingrezza is a medication that is primarily used to treat tardive dyskinesia in adults. It works by regulating dopamine levels in the brain and is taken orally once daily. While it can cause certain side effects, Ingrezza has been shown to be effective in reducing the severity of tardive dyskinesia symptoms. Patients should talk to their healthcare provider to determine if Ingrezza is the right treatment option for them.